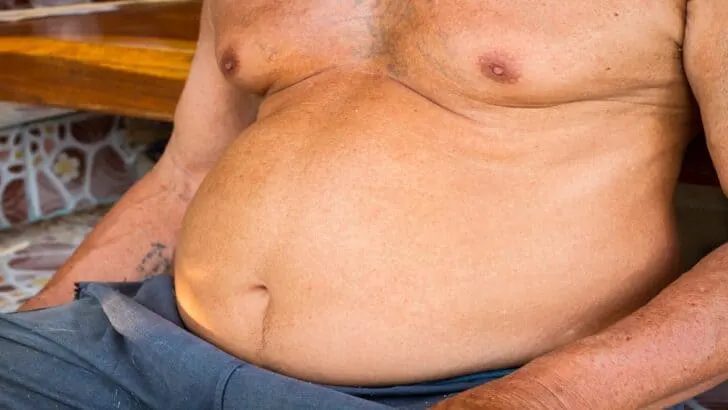
A BMI of 40 falls into the class 3 obesity category, at which point an individual is considered severely obese or morbidly obese.
While different people with a body mass index of 40 will naturally have varying levels of muscle mass, it’s clear that anyone with a 40 BMI is also carrying too much body fat.
Compare Related BMIs:
What does a BMI of 40 look like on a female?

A female with a BMI of 40 looks obese because of her excess body fat. Indeed, a woman who has a 40 BMI is 10+ BMI points heavier than the average lady in America.
Obviously, some women have a lot of muscle mass and/or a large build, which can definitely increase their BMI without harming their health. After all, BMI doesn’t distinguish between muscle and fat. [1]
The problem is that a BMI of 40 is so high that no woman can be lean while walking around with a body mass index of 40.
As such, a BMI 40 woman should talk to her doctor so that they can give her a personal weight loss plan that will work for her body and current situation.
What does a 40 BMI man look like?
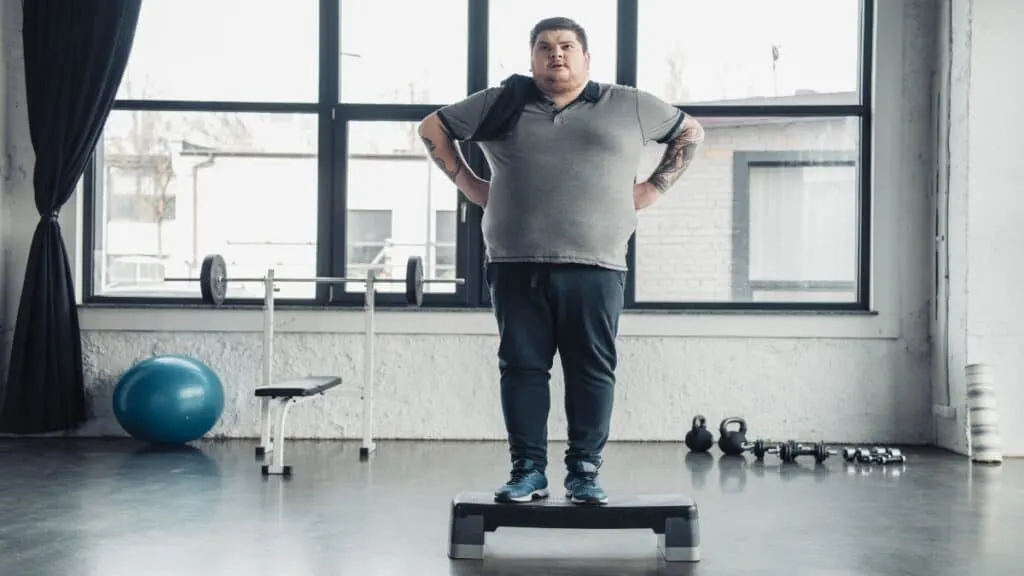

A BMI 40 man looks much heavier and larger than the average man due to his excess body fat. At a hefty BMI of 40, it’s no longer possible for a man to hide his excess body fat.
As noted, a male with a 40 BMI score is considered severely obese, but only just. As such, a man with a BMI of 40 is in a prime position to lose weight before such a task becomes much harder due to extreme obesity.
Obviously, some men can have a lot of muscle mass, which can certainly lead to a high BMI. But as with their female counterparts, no man is going to have a lean 40 BMI because the human body can’t accumulate that much lean mass naturally.
Common BMI 40 results and their classifications

Here are all of the BMI 40 classifications with a brief outline of their degree of obesity.
40.1 BMI
If you’ve got a 40.1 BMI, then you’re just into the class 3 obesity category. Losing weight will move you into the lower obesity classes, which can be motivating to see.
40.2 BMI
A 40.2 BMI, while much heavier than average, is still on the very low end of the severely obese category and can be reduced via doctor-supervised calorie restriction and exercise.
40.3 BMI
If you have a BMI of 40.3, then you’re well into the obese category and are likely harming your health.
40.4 BMI
A 40.4 BMI is very much excessive for men and women who want to enjoy good health due to the fact that obesity often leads to chronic disease in the long term.
40.5 BMI
If you have a BMI of 40.5, then you’re half a BMI point into the class 3 obesity classification.
As such, if you have a 40.5 BMI, you’ll need to lose body fat by exercising regularly and consuming fewer calories so that you can create the energy deficit which is necessary for weight loss.
40.6 BMI
Those who have a BMI of 40.6 are considered severely obese and will need to reduce their body weight by a significant amount if they want to achieve good health.
40.7 BMI
If you’ve got a 40.7 BMI, then your body weight is excessive for a person of your height, even if you’re muscular.
40.8 BMI
A 40.8 BMI is over 10 BMI points higher than usual for American men and women (and the average is already too high).
40.9 BMI
A BMI of 40.9 is very high for both females and males and needs to be reduced by a combination of increased physical activity and moderate-to-aggressive calorie restriction.
FAQ

These are some of the most common questions that people have about a body mass index of forty.
Can you get a tummy tuck with a BMI of 40?
Getting a tummy tuck with a BMI of 40 is likely not a good idea and will probably not be recommended if you intend to lose some of your excess weight. [2]
To be sure, there are good reasons to get a tummy tuck. But the first priority of a BMI 40 individual, if I may say so, should be to achieve a healthy body weight.
After reducing their BMI, then a person can consider image-improving cosmetic surgeries like a tummy tuck.
How much does a BMI 40 person weigh?
A person with a BMI of 40 will always weigh considerably more than average for a person of their height.
But because two people can both have a 40 BMI score while being very different heights, their body weight will naturally differ.
As such, it’s not possible to give a concrete answer in pounds or kilograms regarding the weight of a BMI 40 man or woman.
Why is having a BMI over 40 so bad for your health?
Having a BMI over 40 is very bad for your health because obesity—BMI 40 is considered severely obese—can lead to chronic disease if left untreated.
Major health issues like diabetes, stroke, and heart disease can arise if a person’s weight spirals out of control, and the heavier someone gets, the harder it often is for them to lose weight.
Is a BMI of 40 morbidly obese?
Yes, a BMI of 40 is the first body mass index score to be considered morbidly obese, although a 40 BMI is more commonly referred to as class 3 obesity or simply severe obesity.
The verdict on having a body mass index of 40
While there are a lot of people out there who have a BMI of 40 for a variety of different reasons, such a high body mass index is certainly indicative of, at the very least, an elevated chronic disease risk.
Consider for a moment that people of a normal body weight may be considered obese if they have lots of body fat and very little muscle. [3] These are people with a BMI well under 40.
Knowing this, it appears to be very much true that a 40 BMI score is morbidly obese and therefore requires help from doctors and nutritionists to be brought under control.
References
- Segal, K. R., Dunaif, A., Gutin, B., Albu, J., Nyman, A., & Pi-Sunyer, F. X. (1987). Body composition, not body weight, is related to cardiovascular disease risk factors and sex hormone levels in men. The Journal of clinical investigation, 80(4), 1050–1055. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI113159
- Tummy tuck – Mayo Clinic. (2022, January 20). https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/tummy-tuck/about/pac-20384892
- Romero-Corral, A., Somers, V. K., Sierra-Johnson, J., Korenfeld, Y., Boarin, S., Korinek, J., Jensen, M. D., Parati, G., & Lopez-Jimenez, F. (2010). Normal weight obesity: a risk factor for cardiometabolic dysregulation and cardiovascular mortality. European heart journal, 31(6), 737–746. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehp487